For years, merchants relied on fixed fraud rules and predictable authentication flows to manage risk. A transaction was either safe or unsafe, exemptions were binary, and routing had little influence beyond acquirer availability. But by 2026, this model has collapsed under the weight of fast-moving fraud patterns, stricter authentication requirements and dramatically more complex issuer decisioning.
Fraud no longer behaves uniformly. Attackers use automation, behavioural spoofing, bot-driven velocity bursts, and cross-border triangulation to exploit moments of weakness in the payment flow. At the same time, issuers now operate with advanced behavioural scoring systems, stronger SCA enforcement and corridor-specific risk policies. A static rule created last quarter cannot anticipate an issuer tightening authentication thresholds this morning or a fraud ring testing your BIN mix this afternoon.
This is why the industry has shifted from rules to orchestration, a model where decisions adapt in real time, transaction by transaction. Dynamic risk orchestration brings together AI scoring, SCA exemptions, authentication signals, device intelligence and routing data into one coordinated engine. The goal is no longer to simply stop fraud, but to strike a sustainable balance between protection and conversion.
For high-risk and cross-border merchants, this evolution is essential. Every unnecessary 3DS challenge, mistimed retry or misaligned route can cost approvals, and every over-aggressive risk filter can suffocate growth. Dynamic risk orchestration gives merchants and PSPs the ability to react instantly to issuer behaviour, to apply exemptions safely, and to route transactions in ways that minimise friction without escalating fraud.
In short: payments in 2026 require intelligence, not thresholds. And the merchants that embrace dynamic orchestration will be the ones who convert more customers, reduce fraud efficiently and outperform competitors across every corridor they operate in.
- What Dynamic Risk Orchestration Actually Means (2026 Definition)
- AI-Informed Decisioning: The New Core of Risk Logic
- Real-Time Authentication Decisions: When to Invoke SCA, When to Avoid It
- The 2026 SCA Exemption Engine: A Performance Tool, Not a Compliance Checkbox
- Routing Meets Risk: Orchestrating the Entire Payment Path
- High-Risk Vertical Use Cases (Practical 2026 Scenarios)
- Compliance Challenges: Balancing Innovation With Regulatory Expectations
- KPIs That Define Success in Dynamic Risk Orchestration
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What Dynamic Risk Orchestration Actually Means (2026 Definition)
Dynamic risk orchestration is the evolution of traditional fraud management into a unified decision layer that adapts to each transaction in real time. Instead of treating risk, authentication and routing as separate functions, orchestration connects them into a single system that evaluates dozens of signals within milliseconds before choosing the safest and smoothest path forward.
In earlier payment stacks, a fraud model would score the transaction, a separate logic layer would decide whether to apply SCA, and routing would happen independently through a default acquirer. By 2026, this separation leads to unnecessary friction, inconsistent decisions and lost approvals. Dynamic orchestration fixes this by allowing one engine to weigh risk, authentication requirements, issuer expectations and routing behaviour together.
A dynamically orchestrated transaction works like this: AI first assesses the probability of fraud and predicts how the issuer is likely to respond. Based on corridor rules, BIN behaviour and device intelligence, the system evaluates whether an exemption is safe or whether 3DS is needed. It then determines which acquirer is most likely to approve the payment under current issuer conditions. The final result is a coordinated decision that protects the merchant while avoiding unnecessary friction for the customer.
The value of orchestration lies in its adaptability. When issuer behaviour shifts, when fraud rings become active, or when authentication success drops in a specific region, the system adjusts automatically. Instead of relying on rules that were written once and left unchanged, merchants gain a decision framework that evolves with the environment. This is especially powerful for high-risk and cross-border merchants, who face constant volatility in issuer sentiment and corridor risk profiles.
Dynamic risk orchestration, at its core, ensures two things: the right level of security at the right moment, and the highest possible chance of approval without increasing exposure. It is the bridge between fraud prevention and revenue protection something static rules were never designed to achieve.
AI-Informed Decisioning: The New Core of Risk Logic
Artificial intelligence has become the foundation of modern risk evaluation, replacing the slow, rule-heavy systems that dominated the early years of online payments. Instead of scoring transactions with static velocity checks or geolocation rules, 2026 payment stacks rely on machine-learning models that evaluate behaviour, device patterns, network signals and issuer tendencies in real time.
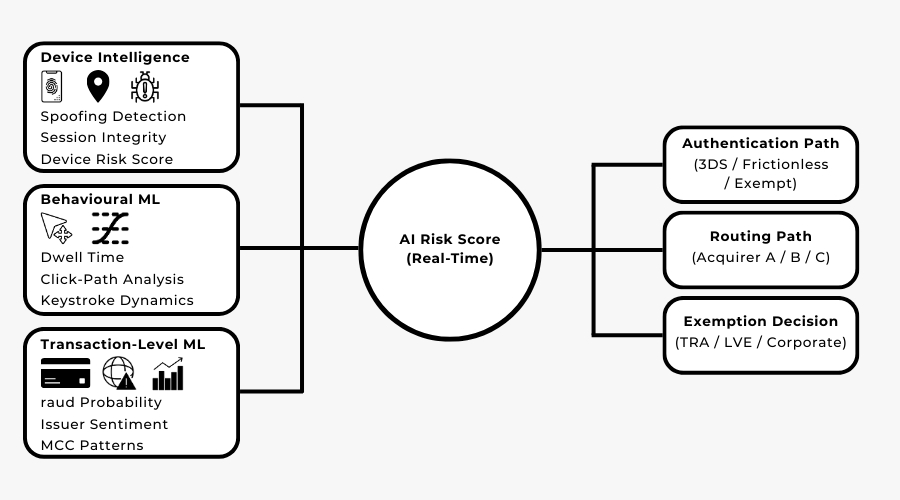
AI now sits at the first layer of the risk orchestration engine. Before a transaction is authenticated or routed, the system predicts two critical probabilities:
- How likely the transaction is to be fraudulent
- How likely the issuer is to approve it under current conditions
These predictions guide everything that follows; whether to apply an exemption, whether to step up authentication, and which acquirer to use.
One major influence on this evolution is regulation. Under PSD2 and the upcoming PSD3/PSR framework, payment service providers are expected to apply strong behavioural analytics and transaction risk analysis to justify SCA decisions. The European Banking Authority (EBA) explicitly states that exemptions can only be used when the provider maintains fraud rates below specific thresholds, reinforcing the need for reliable predictive modelling.
Device Intelligence Models
Device models analyse how trustworthy a device appears across the network. They detect anomalies such as virtualised devices, mismatched geolocation, abnormal session behaviour or cloned device fingerprints. These signals heavily influence whether exemptions are safe or whether 3DS is inevitable.
Behavioural ML Models
Behavioural machine learning examines subtle patterns such as mouse movement, keystroke rhythm, navigation flow, typing cadence and form-fill behaviour. These patterns help distinguish legitimate customers from automated scripts or synthetic identities, especially in high-risk flows like gaming, ticketing and FX trading.
Transaction-Level ML Models
These models provide the “final score” that orchestration engines depend on. They evaluate corridor-based fraud patterns, BIN-level anomalies, merchant history, issuer decline sentiment and even micro-seasonality (e.g., fraud spikes at certain hours).
The result is a dynamic understanding of risk that changes every minute far beyond what manual rules can achieve.
In 2026, AI doesn’t replace human risk teams; it enhances them. It provides the predictive layer needed to balance conversion and protection in a world where fraud evolves faster than static systems can respond.
Real-Time Authentication Decisions: When to Invoke SCA, When to Avoid It
Authentication used to be a simple Yes/No decision: either apply 3DS or skip it. But in 2026, authentication has become a strategic optimisation layer. Merchants must balance fraud prevention, issuer expectations, exemption availability and user experience all in real time. Dynamic risk orchestration brings these elements together so that authentication decisions adapt to the context of each transaction rather than relying on static flows.
One reason this shift has accelerated is regulatory evolution. Under the Strong Customer Authentication rules within PSD2 and reaffirmed in discussions surrounding PSD3 issuers and payment providers must apply authentication proportionately and with sufficient data quality. The European Commission reinforces this expectation by encouraging more consistent and transparent authentication standards across the EU.
This means the decision to authenticate must be grounded in a combination of risk scoring, issuer behaviour and corridor expectations, not just merchant preference.
3DS2 vs. Frictionless Logic
A core component of orchestration is choosing between a frictionless experience or a full 3DS challenge. A frictionless flow is ideal for user experience but only succeeds when the issuer trusts the data provided. If the AI model predicts that a challenge is inevitable for example, because a specific issuer rarely accepts frictionless authentication for certain BINs or transaction types forcing a frictionless attempt can actually trigger a decline.
Conversely, some issuers prefer frictionless flows when risk signals are strong and the transaction context is familiar. Dynamic systems adapt to these issuer preferences, increasing approval rates by avoiding unnecessary challenges.
Tokenisation & Network Data Pathways
Another authentication determinant is the quality of network token data. In 2026, token lifecycle status, device-binding integrity and cryptogram validity significantly influence issuer trust. If the token is fresh, bound to a known device and paired with high-quality metadata, many issuers lower the need for step-up authentication.
Tokenisation also improves reliability across cross-border corridors, where PAN-based transactions often face heavier scrutiny. A strong orchestration engine evaluates token status in real time and adjusts authentication strategy accordingly.
The Practical Outcome: Fewer Friction Moments, Higher Approval Rates
Real-time authentication decisions ensure that customers only face friction when absolutely necessary. For high-risk merchants where issuers already apply additional scrutiny this precision has a major impact. By aligning authentication to issuer expectations, fraud risk and corridor behaviour, PSPs can reduce abandonment, avoid false declines and deliver a more predictable approval environment.
Dynamic orchestration does not eliminate authentication; it optimises when and how authentication occurs. This is the difference between a static rule and an intelligent decision engine.
The 2026 SCA Exemption Engine: A Performance Tool, Not a Compliance Checkbox
In earlier years, SCA exemptions were treated as a compliance convenience something merchants used occasionally to avoid unnecessary friction. By 2026, exemptions have evolved into a core optimisation lever, allowing merchants to preserve conversion while staying within fraud thresholds defined by regulators and card networks.
The most important shift is that exemptions now operate within a risk-managed framework, not a static ruleset. PSPs must justify every exemption through strong Transaction Risk Analysis (TRA), device intelligence, issuer behaviour understanding and corridor-specific fraud rates. This requirement stems from regulatory expectations outlined under the European Union’s evolving payments legislation, including PSD2 and the upcoming PSD3/PSR reforms, where exemption eligibility is tied to fraud performance.
This changes how exemptions are deployed: dynamic risk orchestration decides whether an exemption is safe per individual transaction, not per category.
Low-Value Exemptions (LVE)
In 2026, low-value exemptions still apply to transactions under €50, but the real differentiator is issuer trust. If a merchant’s risk signals are strong and the issuer has high confidence in the corridor, LVE reliably bypasses friction. Poor issuer sentiment, however, can nullify the benefit even for small payments. Dynamic orchestration evaluates BIN patterns, issuer thresholds and fraud scoring to determine if LVE will be honoured.
TRA Exemptions: Now Entirely Data-Driven
TRA (Transaction Risk Analysis) exemptions are the most strategically valuable. When fraud levels fall below regulatory thresholds, merchants can safely send frictionless payments but this is only viable when AI models show high predictive accuracy.
In 2026, TRA decisions depend on:
- Device reputation
- Behavioural patterns
- Issuer-specific exemption history
- Fraud cluster detection
- Cross-border corridor volatility
This means TRA is no longer a blanket policy, it’s a decision made dynamically for each payment attempt.
Corporate Card Exemptions
Corporate environments have distinct spending patterns and strong authentication controls (e.g., internal policy approvals), making them good candidates for exemptions. Orchestration engines detect corporate BINs or token attributes and automatically flag them for exemption where safe.
But even within corporate flows, risk varies by region. Some Middle Eastern and Asian issuers apply stricter authentication regardless of BIN type. Dynamic orchestration ensures exemptions are only attempted where likelihood of approval is high.
Why Exemption Strategy Is Now Essential
In high-risk verticals, issuers already expect additional friction. A poorly timed exemption request can reduce approval rates if the issuer rejects it and initiates an SCA-required decline. Conversely, a well-timed exemption backed by strong AI risk scoring can increase conversion by avoiding unnecessary challenges.
Exemptions are no longer compliance shortcuts; they are core components of a merchant’s revenue strategy. The sophistication of the decision engine directly impacts approval rates, fraud ratios and overall customer experience.
Routing Meets Risk: Orchestrating the Entire Payment Path
In 2026, routing is no longer a technical afterthought that happens once the authentication layer completes. As fraud patterns shift faster and issuer behaviour becomes more dynamic, routing itself has become a core risk decision. Dynamic risk orchestration unifies authentication, exemptions and routing into a single adaptive process ensuring every transaction is sent down the path with the highest likelihood of approval and lowest exposure to fraud.
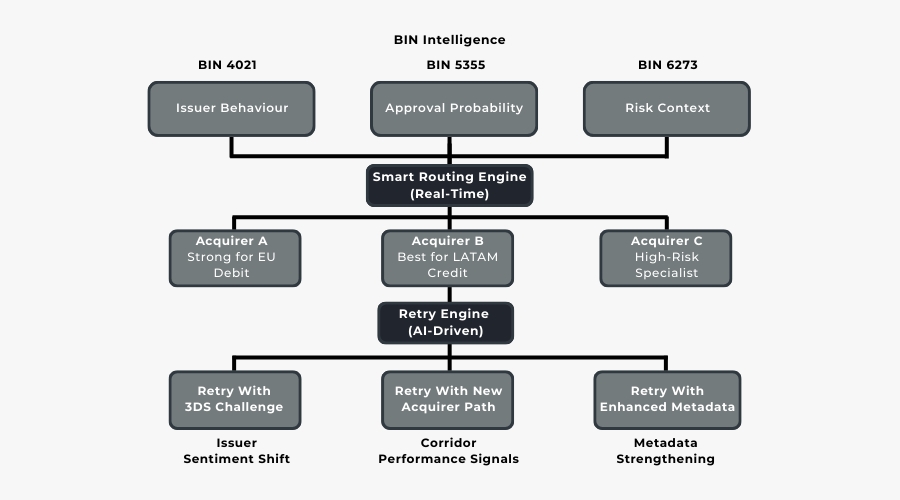
When an AI engine predicts that a specific BIN range is currently sensitive, or when a particular issuer has tightened frictionless acceptance, the orchestrator adjusts routing instantly. Likewise, when authentication outcomes challenge success, frictionless eligibility, exemption safety change in real time, routing adapts with them. This is why PSPs have stopped treating routing as a separate module. Today, it directly shapes both conversion and fraud posture.
BIN-Level Routing Decisions
BIN performance is no longer a static metric. In high-risk and cross-border environments, BIN clusters behave differently depending on corridor, issuer risk appetite, time of day and historical performance. Some acquirers excel with European debit BINs but underperform with APAC credit BINs. Others deliver strong approval rates for specific high-risk MCCs but struggle with cross-border flows.
Dynamic orchestration continually monitors issuer responses, decline patterns and authentication outcomes to determine whether a BIN range should be routed through Acquirer A, Acquirer B or an entirely different PSP. The objective is simple: match each BIN to the acquirer most likely to approve at that moment not yesterday, not last week.
In high-risk verticals this is critical. A poorly matched BIN–acquirer route can reduce approvals by double digits, even when fraud risk is low.
Geography & Corridor-Based Routing
Every region has its own risk dynamics and issuer expectations. European issuers tend to be more predictable but heavily influenced by SCA rules. LATAM corridors face issuer-specific thresholds and local fraud spikes. GCC and APAC regions often favour domestic routing signals and tokenised transactions.
Dynamic orchestration adjusts to these variations by treating geography as a living risk factor. If an orchestrator sees an issuer in Brazil tightening acceptance based on non-domestic acquirer codes, it routes through a provider with stronger domestic recognition. If an EU issuer is currently favouring frictionless flows for specific MCCs, it adapts authentication and routing together to take advantage of the opportunity.
This is where PSD2/PSD3 regulatory expectations also matter. Issuers in Europe must apply Strong Customer Authentication proportionately, which influences how routing paths interact with exemption attempts. The European Banking Authority outlines these expectations here.
Geography is no longer a setting; it is a behavioural signal. And routing decisions evolve dynamically as these behaviours change.
AI-Powered Retry Logic
Retry logic used to be a simple timed repeat: resubmit the transaction with the same data after a short delay. In 2026, such an approach is ineffective and often counterproductive. AI-powered retry logic transforms retries into intelligent second attempts that correct the friction point that caused the initial decline.
If the first attempt failed because the issuer demanded stronger authentication, the second attempt may include 3DS. If the acquirer underperformed for that BIN in the past hour, the retry may route to a different PSP.
If the decline was caused by missing or weak metadata (e.g., inconsistent device signals), the retry may attach enhanced data elements. Each retry becomes a calibrated strategy, not a repetition.
The goal is not to “force” approvals through volume, it’s to address the issuer’s real objection. This is why modern PSPs generate higher approval rates without increasing fraud risk: every retry is informed by risk signals, issuer temperament and corridor conditions.
High-Risk Vertical Use Cases (Practical 2026 Scenarios)
Dynamic risk orchestration becomes most valuable in verticals where fraud velocity, issuer scrutiny and cross-border patterns fluctuate rapidly. High-risk merchants often face unpredictable approval rates, sudden authentication spikes and corridor volatility that traditional risk engines are too slow to manage. The following real-world scenarios illustrate how orchestration reshapes outcomes by aligning risk, authentication and routing decisions at the transaction level.
Gaming & Betting: Balancing Instant Deposits With Fraud Spikes
Gaming operators rely heavily on real-time deposits. Any friction, unexpected 3DS challenges, poorly timed exemptions or issuer sensitivity directly impacts revenue. Fraudsters, meanwhile, exploit fast-deposit environments through bot attacks, card testing and synthetic identities.
Dynamic orchestration helps gaming operators by:
- Detecting device anomalies and behavioural inconsistencies before authentication
- Adjusting frictionless flows during peak fraud windows
- Routing transactions to acquirers with historically better approval rates for specific European or LATAM BINs
- Applying TRA exemptions only when fraud scoring is confidently low
The outcome is a dual improvement: gaming platforms reduce fraud exposure while delivering smooth deposit experiences to genuine players.
Travel: Preventing Ticketing Fraud Without Increasing Abandonment
The travel sector faces two major challenges: high fraud attempts (especially around last-minute bookings) and a high abandonment rate when authentication becomes too intrusive. Issuers tend to scrutinise travel MCCs more aggressively due to historical fraud losses, making routing and authentication decisions unusually unpredictable.
Dynamic orchestration improves travel payments by:
- Detecting “panic-buying” fraud patterns through behavioural ML
- Predicting whether a specific issuer is likely to demand full 3DS
- Routing high-value bookings through acquirers with stronger travel-MCC approval performance
- Reducing unnecessary challenges for frequent or returning customers
This keeps the checkout conversion smooth while blocking sophisticated ticketing fraud bursts.
Forex & CFD: Reducing Recurring Declines and Velocity Loops
Forex merchants experience repetitive issuer friction, especially when customers attempt multiple deposits in a short period or when cross-border MCC sensitivity increases. Static rules often trigger a loop where every subsequent attempt fails for the same reason.
Dynamic orchestration helps by:
- Evaluating issuer-level tolerance for velocity patterns
- Introducing authentication variation (e.g., challenge on 2nd attempt, frictionless on 3rd)
- Routing retries through PSPs that handle high-risk MCCs more effectively
- Adjusting exemption strategies based on real-time risk score changes
For FX firms, this prevents revenue loss caused by repeated declines and improves customer trust in platform reliability.
Digital Entertainment: Managing BIN Volatility Across Borders
Streaming, dating and subscription-based platforms often process cross-border microtransactions, where issuer sentiment varies significantly by geography. BINs originating from SEA, LATAM or Eastern Europe may behave unpredictably depending on corridor and risk context.
Dynamic orchestration stabilises outcomes by:
- Interpreting BIN clusters to determine their optimal routing pathway
- Evaluating which issuers currently favour tokenised transactions
- Applying exemptions selectively based on real-time fraud scoring
- Shifting authentication style depending on device and behavioural signals
This approach reduces false declines and allows digital entertainment platforms to scale globally without losing approval consistency.
Compliance Challenges: Balancing Innovation With Regulatory Expectations
Dynamic risk orchestration delivers extraordinary conversion and fraud-control benefits, but it also introduces new regulatory responsibilities. As PSPs rely more heavily on AI-driven decisioning, adaptive SCA logic and cross-border routing intelligence, regulators increasingly demand transparency, proportionality and robust governance.
By 2026, merchants and PSPs must navigate a world where innovation is encouraged, but only when it aligns with strict compliance expectations. Risk orchestration cannot simply be effective; it must be auditable, explainable and defensible under PSD3, PSR and global AML frameworks.
PSD3 & PSR: Authentication Transparency and Risk Accountability
The upcoming PSD3 and the Payment Services Regulation (PSR) reinforce the requirement that PSPs maintain clear authentication logic and document how exemptions, TRA decisions and delegated authentication models are applied. Regulators want proof that SCA is used proportionately and that exemption strategies are supported by accurate, measurable fraud data.
The European Commission has emphasised the importance of strengthening authentication controls and improving industry-wide fraud resilience, making transparency a core compliance obligation:
In a dynamic orchestration environment, this means every adaptive decision whether frictionless, challenged or exempted, must be explainable retrospectively. PSPs need audit-grade logs demonstrating why a transaction was routed a certain way, why SCA was bypassed or triggered, and how the AI score justified the exemption.
GDPR & AI Governance: Data Minimisation and Explainability
AI-driven risk engines depend on behavioural patterns, device intelligence, issuer trends and transaction metadata. Under GDPR, PSPs must ensure that only necessary data is processed and that AI decisions remain explainable.
This is particularly challenging when orchestration combines hundreds of micro-signals into real-time predictions. Merchants and PSPs must be able to articulate:
- Which data types influenced the risk score
- How AI models were trained
- What safeguards prevent bias or discrimination
- How decisions are reviewed and supervised
As dynamic orchestration grows more complex, so does the obligation to manage models responsibly. The result is a dual mandate: optimise performance while demonstrating regulatory discipline.
Record-Keeping & Audit Trails for AI-Driven Decisions
Perhaps the most demanding requirement of 2026 orchestration is auditability. Regulators and acquiring banks expect merchants, especially those in high-risk categories to retain detailed records of how decisions were made. This includes:
- Why an exemption was used
- How AI contributed to the risk score
- How routing paths were chosen
- Whether customer friction aligned with risk level
PSPs must maintain full event logs showing time-stamped decision paths. If a dispute arises, or if an acquirer questions a merchant’s fraud ratios, these audit trails become essential for defending operational choices.
For merchants, this means working with providers who offer transparent dashboards, clear logs and explainable AI outputs, not “black box” systems. Compliance is no longer an afterthought; it is intertwined with every optimisation decision the orchestrator makes.
KPIs That Define Success in Dynamic Risk Orchestration
Dynamic risk orchestration is only effective when it produces measurable improvements. PSPs and merchants in 2026 no longer evaluate performance through generic metrics like “overall approval rate” or “fraud rate.” Instead, they monitor a set of orchestration-specific KPIs that reveal whether AI scoring, exemption strategies, authentication logic and routing decisions are truly working together.
These KPIs show how well the orchestration engine balances fraud prevention with conversion uplift the two outcomes that define success in high-risk and cross-border environments.
Fraud Rate vs. Exemption Utilisation
One of the clearest indicators of orchestration maturity is how fraud levels behave when exemptions are applied. Strong orchestration allows merchants to increase frictionless volume without exceeding the fraud thresholds required under regulatory frameworks. If fraud rises disproportionately to exemption use, the system’s predictive models require refinement.
A high-performing system maintains fraud at or below corridor thresholds while increasing exemption efficiency, proving that the AI is accurately identifying low-risk transactions.
Approval Rate Uplift After Orchestration Adoption
Approval improvements remain one of the most visible outcomes of dynamic risk orchestration. PSPs typically track uplift by comparing pre-orchestration and post-orchestration approval rates across:
- Specific BIN ranges
- Authentication modes
- Corridors
- Acquirer pathways
A genuine orchestration engine doesn’t just increase approvals broadly, it increases them strategically, especially where issuers have historically been more cautious or inconsistent.
3DS Friction Reduction
Merchants also measure orchestration success by monitoring how frequently customers encounter unnecessary authentication challenges. A strong orchestration layer reduces challenge rates by confidently applying exemptions or selecting the right authentication method for the issuer or corridor.
Success is reflected in lower abandonment, shorter checkout times and fewer failed SCA attempts without increasing fraud exposure.
Routing Efficiency Score
Routing efficiency measures how often the selected acquirer turns out to be the optimal one for the transaction. This metric blends approval likelihood, issuer behaviour, corridor conditions and BIN performance into a single view.
If routing efficiency climbs consistently, it signals that the orchestrator is learning and adapting quickly to real-time conditions.
Latency Impact on Conversion
Dynamic orchestration introduces multiple decision layers AI scoring, authentication selection, routing choice all of which need to execute in milliseconds. High latency undermines even the strongest fraud and authentication logic, especially in high-risk verticals where customers abandon quickly.
PSPs track latency impact by correlating processing times with approval probabilities and checkout completion rates. A well-designed orchestrator improves performance without slowing the transaction down.
Cost Per Accepted Transaction (Adjusted for Fraud)
The final KPI blends financial efficiency with risk posture. A transaction is only valuable if it generates net revenue after fraud losses, routing fees, FX charges, scheme fees and authentication costs.
Dynamic orchestration reduces cost per accepted transaction by:
- Lowering the volume of failed or unnecessary retries
- Improving routing accuracy
- Reducing friction that leads to abandonment
- Minimising fraud losses
This metric often becomes the single most important benchmark for merchants operating thin-margin or high-risk business models.
Conclusion
Payments in 2026 no longer operate on predictable patterns or fixed assumptions. Fraud evolves in real time, issuers continuously adjust their authentication thresholds, and corridor-specific approval behaviour shifts hour by hour. In this environment, static rules and isolated decision systems simply cannot keep up.
Dynamic risk orchestration has emerged as the only sustainable model for merchants and PSPs who need to optimise conversion without compromising fraud resilience. By unifying AI scoring, SCA exemptions, routing intelligence and authentication logic, orchestration transforms each payment attempt into a tailored decision, one that reflects real-time signals, issuer sentiment and the merchant’s risk appetite.
For high-risk and cross-border merchants, the difference is profound. Approvals become more predictable. Authentication friction becomes the exception rather than the rule. Fraud spikes can be neutralised without throttling legitimate customers, and routing finally becomes a revenue lever instead of a passive configuration.
The regulatory landscape is moving in the same direction. PSD3, PSR and global AML frameworks expect risk management to be dynamic, explainable and proportional. Orchestration aligns with these expectations by producing audit-ready decisions and intelligent authentication strategies backed by measurable data.
The future of payments will be defined by the merchants who can adapt not through more rules, but through smarter decisions. Dynamic risk orchestration gives them the operating system they need to navigate an increasingly complex ecosystem while protecting both customer experience and revenue.
In 2026 and beyond, orchestration is no longer an innovation. It is the new default.
FAQs
1. What exactly is dynamic risk orchestration in payments?
ADynamic risk orchestration is a unified decision system that evaluates fraud risk, authentication requirements and routing options in real time. Instead of relying on static rules, it adapts each transaction based on issuer behaviour, AI scoring and corridor conditions to maximise approvals while maintaining fraud control.ns
2. How is orchestration different from a normal fraud engine?
Traditional fraud engines focus only on blocking risky transactions. Orchestration goes further: it connects fraud scoring with SCA decisions, exemptions, token pathways and acquirer routing. This means it doesn’t just prevent fraud it actively improves conversion.
3. Why does issuer behaviour matter so much in 2026?
Issuers now rely heavily on behavioural analytics, corridor-specific fraud data and SCA expectations. Their decision making changes frequently, sometimes hourly. Dynamic orchestration interprets these shifts and adjusts authentication and routing accordingly, preventing unnecessary declines.
4. Can orchestration actually reduce 3DS challenges?
Yes. When AI predicts that a transaction is low risk and when the issuer has a strong exemption acceptance history the orchestrator can safely apply TRA or low-value exemptions, reducing the number of challenges and friction events without increasing fraud.
5. Does using exemptions increase fraud exposure?
Not when exemptions are applied correctly. Orchestration only triggers exemptions when AI models and issuer patterns confirm the transaction is safe. This approach keeps fraud within regulatory thresholds while improving frictionless approval rates.
6. How does routing influence approval rates?
Each acquirer performs differently across BINs, geographies and MCCs. Routing through the wrong acquirer can reduce approvals even when the transaction is legitimate. Orchestration selects the acquirer with the highest real-time approval probability for every transaction.
7. What role does AI play in this system?
AI predicts fraud probability, issuer approval likelihood, exemption safety and routing success. It processes behavioural, device and transactional patterns that humans cannot evaluate at speed or scale. AI provides the intelligence; orchestration executes the decision.
8. How does dynamic orchestration help high-risk merchants?
High-risk verticals such as gaming, travel, FX and digital entertainment face volatile fraud patterns and higher issuer scrutiny. Orchestration stabilises approvals by adapting authentication, exemptions and routing to corridor-specific behaviour, reducing declines and preventing fraud spikes.
9. Will orchestration slow down transaction processing?
Yes, provided the PSP maintains transparent logs, explainable AI models and proportional SCA application. PSD3 emphasises authentication clarity and fraud accountability, which orchestration supports by making every decision auditable and justified.
10. Is dynamic risk orchestration compliant with PSD3 and upcoming regulations?
Yes, provided the PSP maintains transparent logs, explainable AI models and proportional SCA application. PSD3 emphasises authentication clarity and fraud accountability, which orchestration supports by making every decision auditable and justified.
11. Do merchants need specialised systems to support orchestration?
Merchants typically do not need their own infrastructure. Most leading PSPs and orchestration platforms provide plug-and-play decision engines, dashboards and routing tools. However, merchants benefit from keeping clean data, KPI tracking and clear operational workflows.
12. What KPIs should merchants track to measure orchestration success?
Key indicators include approval uplift, fraud rate stability, exemption success, 3DS challenge reduction, routing efficiency, latency performance and cost per accepted transaction. These metrics show whether orchestration is improving both revenue and risk posture.




