In today’s payment landscape, speed, adaptability, and trust define who survives in high-risk verticals such as iGaming, travel, forex trading, nutraceuticals, adult entertainment, and subscription-based services. For merchants in these sectors, the ability to process payments across multiple sales channels, e-commerce checkouts, mobile apps, and virtual terminals (MOTO), has become more than an operational convenience; it is a compliance-driven necessity.
The year 2026 is reshaping payment acceptance in high-risk markets. Regulatory bodies, card networks, and acquiring banks have tightened scrutiny on fraud prevention, chargeback ratios, and data protection. At the same time, customers expect seamless, channel-agnostic experiences: a bettor in Kenya deposits via mobile wallet, a UK forex trader funds an account by card, and a US travel client completes a booking over the phone. Merchants must therefore offer a cohesive, multi-channel payment ecosystem, one that connects every entry point to a single, compliant processing core.
- Channel Architecture at a Glance, What High-Risk-Ready Really Means
- E-Commerce Channel Integration: Building the Backbone of High-Risk Online Processing
- Mobile & In-App Payments: Securing the Next Frontier of High-Risk Processing
- 1. The Rise of Mobile-First High-Risk Transactions
- 2. SDK Integration: Secure, Tokenised, and Fully Auditable
- 3. In-App 3DS2 & Biometric Authentication
- 4. Fraud Prevention in Mobile Environments
- 5. In-App Localisation & Alternate Payments
- 6. Compliance Alignment: PCI, PSD2, and Data Privacy
- 7. Why Underwriters Prioritise Mobile Compliance
- Virtual Terminal (MOTO) Payments: Securing Telephone and Mail Orders in a High-Risk Environment
- Cross-Channel Vetting: Ensuring Unified Risk and Compliance Across E-Commerce, Mobile, and VT Channels
- 1. Why Unified KYC/AML Vetting Matters for High-Risk Merchants
- 2. The Core Architecture of Cross-Channel Vetting
- 3. Compliance Frameworks That Govern Cross-Channel Vetting
- 4. Real-World Example: Cross-Channel Fraud Prevention
- 5. Technical Best Practices for Cross-Channel Integration
- 6. The Underwriter’s Perspective
- 7. Operational ROI: The Hidden Advantage
- Performance Monitoring & Continuous Optimisation: Sustaining Approval Rates Across Acquirers and Regions
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Channel Architecture at a Glance, What High-Risk-Ready Really Means
A modern high-risk merchant cannot rely on a single acquiring connection. Approval rates, fraud exposure, and compliance obligations vary dramatically by country, issuer, and payment type. This section explains the technical foundation of a high-risk-ready gateway, including the multi-acquirer architecture, tokenisation framework, and compliance controls that make it work.
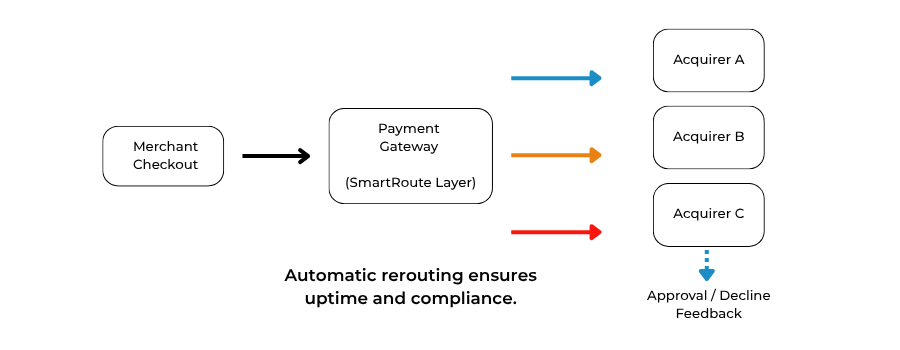
At its core, a gateway is more than a processor, it’s a traffic controller that determines where and how each payment travels. A high-risk gateway, however, operates differently from a standard one: it must continuously balance risk segmentation, approval optimization, and regulatory compliance across multiple sales channels.
1. Multi-Acquirer Architecture: The Foundation of Resilience
In standard low-risk setups, a merchant connects to one acquirer or PSP. If that acquirer declines, the transaction fails outright. High-risk environments can’t afford that vulnerability.
A multi-acquirer gateway uses an orchestration layer that sits between the merchant’s checkout or mobile app and multiple acquiring banks. This structure offers three primary advantages:
- Redundancy: If one acquirer blocks a transaction due to regional or MCC restrictions, the gateway automatically routes to another acquirer.
- Optimisation: Each acquirer has different strengths, some excel in domestic African card acceptance, others specialise in EU e-commerce. Smart routing directs traffic to the acquirer most likely to approve.
- Regulatory Flexibility: For high-risk sectors (e.g., iGaming, nutraceuticals, or adult content), different acquirers hold different risk appetites. Multi-acquirer support allows Payment Mentors clients to distribute transaction load safely without breaching scheme thresholds.
Example: A gaming operator licensed in Malta may process EU card traffic via a local acquirer compliant with the Malta Gaming Authority, while simultaneously sending African wallet transactions to a licensed PSP connected to PayShap (South Africa) or M-Pesa (Kenya).
This model isn’t theoretical, it reflects how major high-risk PSPs like Nuvei, Panda Gateway, and PayRetailers architect their multi-acquirer stacks. Each uses load-balancing logic and API orchestration layers to maintain uptime and compliance across regions.
2. Tokenisation Everywhere: Security Meets Conversion
Tokenization is the backbone of multi-channel security. It replaces sensitive card or wallet data with a unique encrypted token stored in a secure vault.
For high-risk merchants, tokenisation serves two vital purposes:
- Security: It ensures no channel (web, mobile, or TV) ever stores raw PAN data, critical for PCI DSS 4.0.1 compliance and breach mitigation.
- Conversion: By securely storing tokens, merchants can enable one-click deposits or recurring transactions without re-entering card details, reducing friction and abandonment rates.
Payment Mentors recommends deploying a network-token-first strategy, where gateway tokens map directly to Visa, Mastercard, or Amex network tokens. Network tokens dynamically refresh when card details change, maintaining continuity and improving approval rates by up to 5-10% (Visa Data, 2025).
Implementation Tip: Integrate tokenisation at the gateway level rather than in the merchant app. This keeps the cardholder data environment (CDE) outside your infrastructure, reducing PCI scope.
3. Unified Routing Logic: One Brain for All Channels
A high-risk-ready gateway treats each channel, web, mobile, and VT, not as separate silos but as nodes in a single intelligent routing framework.
When a payment request is initiated, the gateway’s routing engine evaluates rules such as:
- BIN country match (e.g., route UK-issued cards to UK acquirers for better approval).
- Transaction type (CIT vs MIT).
- Payment channel (e.g., VT flagged as MOTO to avoid incorrect SCA challenges).
- Historical acquirer performance (approval rates, soft-decline ratios, latency).
These rules feed into Smart Routing and Cascading Logic: both of which we’ll explore in later sections, but it’s the underlying architecture that makes such precision possible.
4. Compliance Alignment Across Channels
One of the biggest challenges in high-risk operations is ensuring that compliance frameworks, PCI DSS, PSD2, AML, and data privacy, apply consistently across all channels.
A properly architected high-risk gateway accomplishes this by:
- Unifying authentication: applying the same risk scoring and 3DS logic across web and mobile checkouts.
- Centralising audit trails: storing transaction, KYC, and risk logs in a single repository for regulatory inspection.
- Standardising encryption: TLS 1.3 for all API endpoints and mutual TLS (mTLS) for inter-server calls.
- Reusing verified customer data: a cross-channel identity system ensures that KYC verified on mobile is valid for VT or e-commerce withdrawals.
This kind of consistency is what acquirers and underwriters look for. Disjointed systems are red flags during onboarding reviews.
5. Channel-Specific Risk Matrix (Compliance Lens)
| Channel | Primary Risk Vector | Compliance Requirement | Mitigation Strategy |
| E-commerce | CNP fraud, account takeover | PSD2/UK SCA, 3DS2 | Device fingerprinting, dynamic 3DS exemption management |
| Mobile | SDK spoofing, app cloning | PCI DSS 4.0.1 + wallet tokenisation | SDK attestation, biometric SCA |
| Virtual Terminal (MOTO) | Agent fraud, data leakage | PCI DSS 4.0.1 MOTO exemption | Secure input fields, call masking, agent role-based access |
This table, drawn from PCI SSC and European Banking Authority guidance, shows that risk in high-risk sectors doesn’t come from volume alone, it’s the channel behaviour that defines exposure.
6. Why High-Risk Gateways Demand Data-Driven Control
The difference between a compliant multi-channel setup and a failing one often lies in monitoring. Real-time dashboards showing approval rates per acquirer and per channel allow merchants to identify failing banks or geographies quickly.
Modern orchestration platforms (e.g., BridgerPay, Panda Gateway, Payment Mentors’ SmartRoute Engine) use machine learning to evaluate the best-performing routes based on time of day, issuer, and transaction profile. For high-risk merchants, this visibility is critical, one blocked region or acquirer can translate into thousands in lost turnover.
E-Commerce Channel Integration: Building the Backbone of High-Risk Online Processing
For high-risk merchants, the e-commerce payment channel is where the real underwriting story begins.
When a bank, PSP, or compliance officer reviews an application, the first thing they evaluate isn’t your revenue potential, it’s your website checkout. That single flow represents your governance, technical control, and consumer protection standard.
And in high-risk sectors such as iGaming, forex, nutraceuticals, and digital content, even one sign of a weak checkout, broken SSL, missing refund terms, inconsistent billing descriptor, can move your file from review to reject in seconds.
1. Why the E-Commerce Gateway Defines Your Underwriting Outcome
Underwriters interpret your website structure as a risk map. They check if your business model aligns with scheme rules, PSD2, and PCI DSS standards.
- Clean Checkout Flows: A secure, hosted payment page (PCI DSS 4.0.1 compliant) signals maturity. Direct card capture on a merchant’s domain, without hosted fields, signals exposure.
- Visible Legal Entity: If your website doesn’t clearly display the business name, licence, or jurisdiction, acquirers treat this as a red flag under FATF Recommendation 15 (digital transparency).
- Aligned Content & KYC: If your KYC form collects more data than required or appears informal (Google Forms, for instance), underwriters question your data protection alignment.
Clean Checkout Flows
A secure, hosted payment page (PCI DSS 4.0.1 compliant) signals maturity. Direct card capture on a merchant’s domain and without hosted fields.
Visible Legal Entity
If your website doesn’t clearly display the business name, licence, or jurisdiction, acquirers treat this as a red flag under FATF Recommendation 15.
Aligned Content & KYC
If your KYC form collects more data than it required or appears informal (Google Forms, for instance) also underwriters question your data protection alignment.
According to Visa’s 2025 Merchant Risk Review Report, 70% of rejected high-risk applications failed not due to industry type, but due to non-compliant website environments.
That is why Payment Mentors treats e-commerce integration as the audit anchor, the point where every technical and compliance strand of your gateway strategy begins.
2. Building for Compliance and Conversion, Not Just Acceptance
In a high-risk ecosystem, the goal isn’t simply accepting cards, it’s accepting them legally, securely, and at scale.
To achieve that, Payment Mentors recommends a compliance-by-design checkout structure, which includes:
| Compliance Pillar | Requirement | Why It Matters for High-Risk |
| PCI DSS 4.0.1 Hosted Fields | Card data never touches merchant server | Reduces PCI scope; passes acquirer audit |
| Transparent T&Cs, Refunds | Must appear before payment step | Required under Visa/Mastercard Acquirer Rule 14.1 |
| SCA (3D Secure 2.x) | Mandatory under PSD2 | Enables acquirer exemptions; protects from chargeback reversals |
| Fraud Monitoring | Device ID, velocity, and IP filters | Reduces dispute-to-sale ratio below 1% |
| Tokenisation | Reuse payment credentials securely | Improves approval rate; essential for subscriptions |
Why this matters: Every one of these factors directly maps to underwriting scorecards used by EU, UK, and offshore acquirers (including those in Malta, Cyprus, and Curacao).
A well-integrated checkout demonstrates readiness. A fragmented or generic gateway suggests unpreparedness, and that’s when acquirers impose high rolling reserves or even deny onboarding.
3. Dynamic 3-D Secure (SCA) and Approval Optimisation
Strong Customer Authentication (SCA) under PSD2 was designed to reduce fraud, but in high-risk segments, rigid implementation often reduces approval rates instead. To counter this, global gateways use smart exemption logic.
Payment Mentors’ orchestration framework dynamically applies exemptions such as:
- LVP (Low-Value Payment): for micro-deposits under €30.
- TRA (Transaction Risk Analysis): bypassing full SCA for low-risk, repeat users.
- MIT (Merchant-Initiated Transactions): for recurring billing or re-deposits.
- Trusted Beneficiary: for loyal, verified users.
These are applied using rule-based routing connected to acquirer performance data.
For instance, a forex client in London saw their approval rate rise from 78% to 91% after Payment Mentors introduced adaptive 3DS routing across UK and EU acquirers, leveraging TRA and MIT exemptions.
SCA isn’t about security alone, it’s about using the regulation as a performance tool.
4. Fraud and Chargeback Defence
In high-risk sectors, fraud is not just a probability, it’s an expectation.
Data from Mastercard’s 2024 High-Risk Chargeback Index shows that iGaming, forex, and subscription models account for over 40% of all global CNP disputes.
To mitigate, a layered defence stack must be implemented at the e-commerce entry point, including:
- Device Fingerprinting: Identifies unique browsers or devices for each transaction.
- Geo-IP Validation: Flags geographic mismatches (e.g., UK card used in Nigeria).
- Velocity Rules: Limits per-card and per-IP attempts.
- Machine Learning Models: Predicts abnormal patterns using acquirer approval feedback.
- Blacklist/Whitelist Sync: Centralised across e-commerce, mobile, and TV channels.
Payment Mentors’ analytics engine integrates all these into a real-time fraud feedback loop, allowing acquirers to adjust exposure thresholds dynamically.
The result? Reduced rolling reserves, improved reputation, and measurable chargeback savings.
5. User Experience (UX): The Forgotten Compliance Factor
Underwriters increasingly assess UX as a regulatory indicator, not just a design element.
A confusing checkout or hidden pricing structure signals poor consumer protection.
Best practices Payment Mentors enforces:
- Plain English copy: Aligns with UK’s Consumer Rights Act (CRA 2015) and FCA Treating Customers Fairly (TCF).
- Local currency visibility: Avoids cross-border disputes caused by FX conversion.
- Accessible refund policy: Must be one click away during checkout.
- Multi-channel continuity: A failed card payment should seamlessly redirect to mobile wallet or VT, never a dead end.
By applying these UX standards, one Payment Mentors client in Ghana reduced support tickets by 36% and saw a 22% increase in successful re-deposits within 30 days.
Mobile & In-App Payments: Securing the Next Frontier of High-Risk Processing
If e-commerce represents the compliance face of your business, mobile and in-app payments are its operational engine. In 2025, over 68% of high-risk transactions in Africa, the Middle East, and Asia originate from mobile channels, not desktop. For high-risk verticals like iGaming, forex, or digital trading, mobile checkout is now the primary revenue driver, yet also the most scrutinised by acquirers.
Mobile transactions carry higher fraud potential, more data privacy risk, and stricter user verification requirements. Therefore, integrating mobile payment channels isn’t just about SDKs and APIs, it’s about creating a secure, tokenised, compliant ecosystem that satisfies regulators while delivering instant experiences for users.
1. The Rise of Mobile-First High-Risk Transactions
Markets across Africa, Asia-Pacific, and Latin America have leapfrogged traditional banking infrastructure.
In countries such as Kenya, Ghana, and Nigeria, over 75% of all online bets and forex trades are initiated via smartphones, primarily using mobile wallets and embedded browser checkouts. Even in Europe, the UK Gambling Commission notes that mobile devices now account for 61% of all gaming interactions (UKGC Annual Report, 2025).
However, this mobile boom introduces unique underwriting challenges:
- Device-level fraud (SIM swaps, rooted devices, spoofed OS versions)
- Regulatory fragmentation (POPIA in South Africa vs GDPR in Malta)
- App-store policy risks (especially for gaming and high-risk financial products)
For underwriters, the mobile channel is a litmus test of a merchant’s digital hygiene, how securely data is transmitted, how identity is verified, and how easily transactions can be reversed.
2. SDK Integration: Secure, Tokenised, and Fully Auditable
A compliant mobile integration starts at the SDK (Software Development Kit) level.
Most acquirers and gateways (including Payment Mentors) now offer SDKs for Android and iOS that include embedded PCI DSS 4.0.1 controls.
These allow the merchant app to capture payment data without storing or transmitting sensitive PAN details directly.
Key SDK Security Standards:
| Control Layer | Standard/Protocol | Purpose |
| Tokenisation | PCI DSS 4.0.1, Req. 3 | Replaces PAN with token for recurring use |
| Data-in-Transit Encryption | TLS 1.3 | Protects against man-in-the-middle attacks |
| SDK Attestation | OWASP MASVS | Confirms SDK not modified or repackaged |
| mTLS Authentication | RFC 8705 | Ensures gateway <-> app mutual validation |
Each SDK is sandbox-tested by Payment Mentors’ compliance team before deployment to ensure it meets both scheme (Visa/Mastercard) and local regulatory requirements (e.g., Central Bank of Nigeria’s digital payment compliance circular, 2025).
This layered protection reduces PCI scope, strengthens acquirer confidence, and provides underwriters with verifiable documentation during merchant review.
3. In-App 3DS2 & Biometric Authentication
Mobile apps provide a unique advantage over desktop web: built-in device biometrics.
Instead of traditional one-time passwords, merchants can leverage biometric 3D Secure (3DS2) challenges, such as fingerprint or facial ID, to meet SCA requirements while improving conversion rates.
- Frictionless flow: Returning users can authenticate using their device’s secure element.
- Fewer false declines: Device binding helps acquirers recognise returning cardholders, improving approval rates by up to 11% (Visa Risk Insights, 2025).
- Strong SCA compliance: Biometric 3DS2 satisfies PSD2 SCA requirements using possession + inherence factors.
For high-risk merchants, biometric 3DS2 isn’t just a UX upgrade, it’s an underwriter-approved risk control.
Payment Mentors’ SDK framework integrates natively with issuer-side ACS providers to ensure biometric challenges align with acquirer region and scheme.
4. Fraud Prevention in Mobile Environments
Mobile introduces fraud vectors that don’t exist in browser-based environments. Underwriters classify them under device-originating anomalies, which include:
- Device emulators mimicking real phones.
- Fake mobile apps designed to phish credentials.
- SIM-swap fraud targeting one-time password flows.
To mitigate these, Payment Mentors’ mobile orchestration platform embeds Mobile Risk Scoring (MRS), a rules-based engine analysing 50+ device attributes, such as:
- Root/jailbreak status
- OS integrity checksum
- Device timezone vs. IP mismatch
- Accelerometer motion data (distinguishes bots)
- SIM carrier validation (for regional compliance)
The MRS engine is certified under EMVCo 3DS 2.3 specifications, ensuring that mobile-originating transactions are fully auditable in case of disputes or chargebacks.
5. In-App Localisation & Alternate Payments
Localisation is the difference between approval and abandonment in mobile payments.
For instance:
- In Kenya, players expect M-Pesa STK push as default, not card forms.
- In Nigeria, the preferred path is USSD or local bank wallet.
- In Brazil, PIX instant payments outperform cards by 3:1 for gaming payouts.
Payment Mentors API aggregation allows these local rails to be embedded directly inside apps, meaning the player never leaves the merchant environment.
Each integration is designed with seamless API fallback to handle wallet downtime, routing to alternate acquirers automatically through cascading logic (covered later in Section 6).
This hybrid strategy, blending global card networks with localized instant payment options, allows merchants to maintain 95%+ uptime and build regional trust with regulators.
6. Compliance Alignment: PCI, PSD2, and Data Privacy
For high-risk operators, mobile compliance must be multi-jurisdictional by design.
This includes aligning:
- PCI DSS 4.0.1 (card data handling).
- PSD2/UK SCA (authentication).
- GDPR/POPIA/NDPR (data privacy).
- Local licensing (MGA, Curacao eGaming, Nigeria’s NLRC).
Payment Mentors maintains a Global Compliance Registry for clients, mapping each app environment to the applicable laws of its operating jurisdiction.
For example:
- A Curacao-licensed iGaming app with Nigerian players must comply with NDPR (Nigeria Data Protection Regulation) and provide user opt-out notices under EU GDPR Article 49.
- A South African trading app processing through PaySharp RTP must meet POPIA Section 19(2) for data integrity.
By maintaining transparent jurisdictional documentation, Payment Mentors ensures that each integration stands up under audit, whether from a regulator, acquirer, or card scheme.
7. Why Underwriters Prioritise Mobile Compliance
Underwriters assess mobile environments more rigorously than desktop because mobile is harder to control.
Their checklist includes:
- Verified SDK security documentation.
- MRS (Mobile Risk Score) history.
- Proof of app-store legitimacy and compliance (no restricted content).
- Alignment of in-app brand, website brand, and corporate entity (to prevent shell operations).
Merchants with inconsistent app-store details or unverified SDK environments often face mandatory reserves or outright rejection.
Payment Mentors underwriting support division therefore includes Mobile Audit Reports, summarising SDK attestation, PCI validation, and MRS output for submission to acquiring partners, reducing review time and increasing acceptance odds.
Virtual Terminal (MOTO) Payments: Securing Telephone and Mail Orders in a High-Risk Environment
In an increasingly digital ecosystem, Virtual Terminal (VT) or MOTO (Mail Order / Telephone Order) payments might sound old-fashioned, yet for high-risk merchants, they remain essential.
From VIP player deposits to recurring client renewals and call-centre upsells, VT transactions bridge the gap between human service and secure digital processing.
But they also sit at the intersection of convenience and compliance risk. Unlike e-commerce or mobile payments, VT transactions are card-not-present (CNP) and non-authenticated, making them prime targets for chargebacks, PCI breaches, and regulatory scrutiny.
For acquirers and underwriters, this is one of the highest-risk sales channels, and without strict controls, it can single-handedly compromise your entire merchant account.
1. What Is a Virtual Terminal: and Why It’s Still Relevant
A Virtual Terminal is a secure web-based payment interface that allows staff to manually key in customer card details.
This channel is widely used in:
- Call centres for inbound deposits or orders,
- Subscription renewals (health, education, coaching),
- VIP or high-ticket processing (forex, events, consultancy),
- Fallback processing when the customer can’t complete an online payment.
For high-risk verticals such as iGaming, coaching, adult, or nutraceuticals, VTs provide an invaluable backup for customer conversions, but only when deployed within strict PCI DSS and KYC frameworks.
2. PCI DSS Compliance: The Non-Negotiable Foundation
The PCI DSS 4.0.1 standard clearly outlines that MOTO environments are within SAQ C-VT scope, meaning the business must prove:
- All terminals are web-based (not locally installed software).
- The system does not store raw cardholder data.
- The connection uses HTTPS with TLS 1.2+ encryption.
- Audit logs are maintained for every transaction.
A compliant Virtual Terminal (like Payment Mentors’ VT Gateway) uses tokenisation and role-based access control (RBAC) to ensure that:
- No card data ever enters merchant systems.
- Agents only view masked PANs.
- Management dashboards provide real-time monitoring of access and edits.
Underwriters specifically request proof of PCI validation during risk assessment, often asking for screenshots of masked input fields and log history as evidence.
3. Risk Controls: Turning MOTO Into a Trust Channel
Because MOTO lacks 3D Secure authentication, acquirers rely heavily on risk controls and operational governance. High-risk operators must deploy multi-layer safeguards to mitigate fraud and maintain acquirer trust:
| Control Type | Implementation Example | Purpose |
| Call Recording & Verification | Log all calls, capture consent for transactions | Creates audit trail for chargeback disputes |
| Agent ID Tracking | Unique login for each operator | Detects internal misuse or error |
| Dual Authentication | Manager confirmation for high-value amounts | Prevents fraud and unauthorised use |
| Customer Identity Verification | Request government ID for large-value MOTO deposits | Satisfies AML/KYC and protects underwriter |
| Geo-Risk Alerts | IP tracking for agent login | Flags unauthorised offshore access |
When these are built into a VT system, underwriters classify the environment as controlled rather than exposed, significantly reducing imposed rolling reserves.
4. The Human Factor: Agent Training & Compliance Culture
The human element is both the greatest asset and the greatest risk in VT processing. A well-trained operator can recover a failed payment with empathy and compliance. A poorly trained one can create a PCI breach within seconds.
Every Payment Mentors VT deployment includes an Agent Compliance Training Pack, covering:
- Securely verifying cardholders before processing.
- Avoiding sensitive data entry in call notes.
- Logging every transaction outcome in CRM.
- Recognising high-risk behaviour (multiple card attempts, mismatched billing data, etc.).
This is not just operational best practice, it’s also a mandatory due diligence requirement under FATF Recommendation 16 (electronic fund transfers).
Acquirers routinely audit call logs and CRM trails for proof of training and traceability before renewing high-risk merchant agreements.
5. Integrating VT with E-Commerce and Mobile Channels
The best VT systems are not standalone; they are extensions of your existing payment gateway, feeding into the same fraud filters, routing rules, and customer database.
This integration enables:
- Unified Transaction History: all VT, web, and mobile payments appear under one client profile.
- Cross-Channel Risk Detection: repeat fraud attempts on the web instantly block MOTO access.
- Consistent Descriptor Use: prevents chargeback confusion from mismatched billing names.
Payment Mentors’ gateway uses multi-channel token orchestration, meaning a card token used on e-commerce can be safely re-applied in VT with customer consent, maintaining PCI scope and improving UX.
6. AML/KYC Integration for VT Transactions
AML compliance in MOTO environments is especially strict because of the manual nature of payments.
Operators must verify customer identity before accepting a card deposit, even over the phone.
Payment Mentors’ VT includes automated KYC verification via linked CRM, which checks:
- Cardholder name vs. ID document.
- Address match vs. billing data.
- Transaction amount against AML thresholds.
If the VT operator attempts a transaction above preset limits or from a flagged customer, the system automatically requires manager approval or triggers AML escalation, ensuring every MOTO transaction is defensible in an audit or underwriter review.
7. Underwriter Perspective: Why VT Still Raises Flags
Underwriters view MOTO transactions through a unique lens. They are often categorised as non-authenticated, elevated exposure because they bypass consumer-side verification.
This leads to:
- Higher default reserves (5-10%).
- Closer rolling reserve monitoring.
- Monthly risk reporting requirements.
However, when merchants demonstrate robust audit controls and data segregation, many acquirers waive VT penalties after a stable 90-day performance window.
Payment Mentors underwriting team works directly with acquirers to present VT control documentation, including PCI SAQ C-VT validation, call audit reports, and access logs, ensuring the business is treated as structured, not speculative.
Cross-Channel Vetting: Ensuring Unified Risk and Compliance Across E-Commerce, Mobile, and VT Channels
In the high-risk payment landscape, the greatest risk doesn’t come from transactions themselves, it comes from inconsistency.
When your e-commerce gateway, mobile app, and Virtual Terminal all handle KYC, AML, and fraud checks separately, you create blind spots. And underwriters hate blind spots.
Cross-channel vetting ensures that every transaction, whether web, mobile, or MOTO, operates under a single compliance framework. This is the difference between a fragmented merchant and a risk-coherent merchant.
1. Why Unified KYC/AML Vetting Matters for High-Risk Merchants
In traditional low-risk retail, KYC is a one-time process. But in high-risk sectors (gaming, trading, adult content, nutraceuticals), ongoing customer verification is a non-negotiable requirement.
Acquirers and regulators expect merchants to prove that their user vetting is:
- Consistent across all channels (no weaker verification path).
- Documented and traceable (every update logged).
- Linked to AML transaction monitoring.
A 2024 Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) report revealed that over 55% of high-risk merchant terminations occurred because of inconsistent KYC verification flows across payment channels.
That’s why underwriters now request an End-to-End Customer Journey Map, showing how the same user identity is validated and monitored across desktop, app, and VT systems.
Payment Mentors implements this through an Omnichannel Compliance Framework that binds every payment entry point under a unified vetting layer.
2. The Core Architecture of Cross-Channel Vetting
At its simplest, cross-channel vetting is the single source of truth for identity and risk.
All systems, e-commerce, mobile, and VT, pull data from and push updates to a central compliance engine.
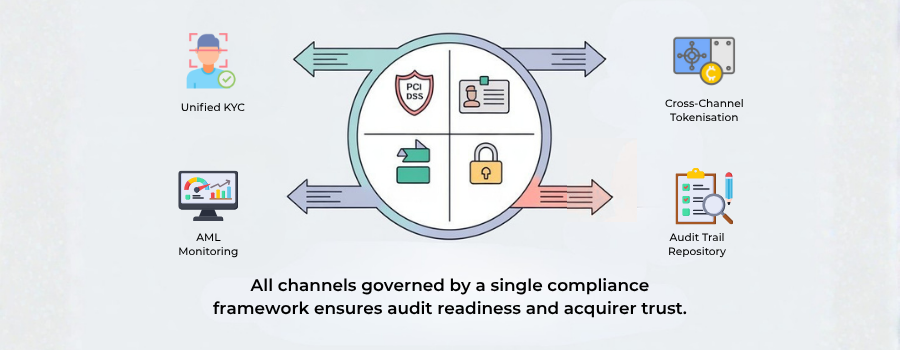
Here’s how it works technically:
- Customer Initiation: When a user registers or makes a first payment, the KYC engine collects ID, address, and risk metadata (IP, device, BIN, geolocation).
- KYC Validation: Documents are verified using OCR and AML database lookups (e.g., World-Check, Refinitiv, or ComplyAdvantage).
- Tokenization & Binding: Once approved, the user is assigned a Compliance Token. This token follows the user across channels, e-commerce, app, or MOTO, ensuring identical risk identity.
- Ongoing AML Monitoring: Each transaction is checked against velocity, transaction size, and behavioural history (e.g., sudden value jumps or repeated failed attempts).
- Cross-Channel Alerts: If suspicious activity is detected on one channel (say, mobile), the same token triggers real-time holds across all others.
This framework removes redundant verification steps and gives acquirers full traceability of identity-to-transaction, dramatically improving underwriter comfort and approval ratios.
3. Compliance Frameworks That Govern Cross-Channel Vetting
To standardise this approach, Payment Mentors aligns with the following global regulations and guidelines:
| Regulatory Body | Guideline/Framework | Relevance |
| FATF | Recommendation 10 – Customer Due Diligence | Global KYC/AML verification rule |
| EU AMLD6 / UK MLR 2025 | Ongoing due diligence for high-risk clients | Applies to licensed gaming & financial services |
| GDPR / POPIA / NDPR | Cross-border data transfer and consent | Data protection for African & EU merchants |
| PCI DSS 4.0.1 | Tokenisation & secure storage of KYC-linked card data | Ensures traceability without exposure |
| MGA & Curacao eGaming | Player verification & payout linkage | Ties compliance to licensing jurisdiction |
Every region defines high-risk differently, but they all share the same core expectation: data consistency and auditability. When a merchant can prove that every channel shares one compliance logic, acquirers reduce reserves and settlement holdbacks.
4. Real-World Example: Cross-Channel Fraud Prevention
Let’s consider a real case:
A Payment Mentors client, an EU-licensed forex broker operating across web, app, and call-centre channels, faced rising chargebacks (2.1%) due to duplicate account sign-ups.
By integrating a cross-channel KYC token system, they unified user identity across all payment interfaces.
If a customer tried to register on mobile after failing on the web, the system recognised the biometric and device match, flagged the transaction, and locked the profile.
Results within 90 days:
- Fraud incidents dropped 64%.
- Chargeback ratio fell to 0.8%.
- Approval rates improved 12% (acquirer reclassified the merchant as moderate risk).
The outcome proved what underwriters often emphasise: identity consistency equals reduced perceived risk.
5. Technical Best Practices for Cross-Channel Integration
To achieve this level of consistency, Payment Mentors mandates the following developer-level practices:
- Centralised API Gateway: All payment and KYC APIs must route through a unified gateway (no direct third-party endpoints).
→ Benefits: easier encryption, logging, and rule enforcement. - Token-Based Identity Linking: Each verified customer should have one persistent token linked to their KYC profile.
→ Benefits: traceable, prevents duplicate onboarding. - Real-Time AML Triggers: Set automated triggers for abnormal transaction behaviour across any channel (large jumps, unusual login times).
→ Benefits: compliance with AMLD6 Article 13(2). - Data Privacy Synchronisation: Ensure all channels use consistent consent terms (e.g., GDPR Article 7 compliance).
→ Benefits: audit readiness and regulator trust.
When all systems speak the same language, every risk event becomes visible, traceable, and resolvable in real time.
6. The Underwriter’s Perspective
When underwriters review your application, they’re not only evaluating your revenue potential, they’re assessing how connected your compliance framework is.
They’ll ask questions like:
- Can a player’s payout ID be reconciled to their deposit token?
- Is your fraud score unified or per-channel?
If the answer is yes, with evidence, your underwriting profile strengthens instantly. Unified compliance frameworks reduce perceived operational risk and, consequently, improve your odds of lower rolling reserves and faster settlements.
As one senior underwriter from a Malta-based acquirer put it:
We don’t fear volume, we fear fragmentation. The more consistent the merchant’s ecosystem, the safer we feel releasing funds.
7. Operational ROI: The Hidden Advantage
While cross-channel vetting improves compliance, it also directly improves business performance:
- Reduced chargebacks: fewer identity errors and duplicate disputes.
- Higher approval rates: acquirers trust unified KYC data.
- Faster onboarding: regulators approve quicker when documentation is centralised.
- Better CX: customers experience seamless verification across web, mobile, and phone.
Payment Mentors reports that merchants with cross-channel KYC tokens experience 28-35% lower manual review time and up to 40% faster payout clearances due to improved traceability.
Performance Monitoring & Continuous Optimisation: Sustaining Approval Rates Across Acquirers and Regions
Once your payment gateway is live and processing, your job is not done. For high-risk merchants, this is where the real battle begins, maintaining stable approval ratios, consistent acquirer uptime, and predictable settlements.
Every underwriter knows that high-risk payment performance can change overnight. One chargeback spike, a regional acquirer outage, or a BIN mismatch can drag your approval rate from 87% to 58% in a single week.
To prevent that, Payment Mentors builds continuous monitoring frameworks that turn performance data into proactive decision-making tools.
1. The Role of Real-Time Performance Monitoring in High-Risk Operations
Traditional merchants can afford to check performance weekly. High-risk merchants cannot.
Why? Because acquirers adjust their internal fraud filters dynamically, often several times a day.
If your system isn’t tracking declines in real time, you’re always reacting late.
A high-risk monitoring suite must track:
| Metric | Why It Matters | Typical Frequency |
| Approval rate by acquirer | Identifies weak or throttled banks | Every 10 min |
| Decline reason codes | Detects BIN or geo mismatch | Real time |
| Chargeback rate by channel | Flags UX or communication issues | Hourly |
| Latency per transaction | Signals gateway or acquirer slowdown | Continuous |
| FX spread variance | Reveals cross-border cost leakages | Daily |
This allows Payment Mentors’ risk analytics team to spot operational risks before they escalate into account terminations.
2. Intelligent Data Orchestration: Turning Raw Data into Action
Raw data means nothing without context. To truly optimise performance, you must connect performance analytics with operational logic.
Payment Mentors’ proprietary Aegis Performance Layer does exactly this, integrating gateway logs, acquirer feedback, and decline reason codes into one visual intelligence suite.
How it works:
- Data Aggregation: Collects live metrics from every acquirer and payment channel.
- Anomaly Detection: Identifies outlier trends like sudden Do Not Honour or Generic Decline codes.
- Root Cause Correlation: Cross-references with geo-data, time-of-day, and transaction type.
- Auto-Optimisation: Pushes new routing rules or acquirer prioritisation updates in real time.
Example: If EU BIN declines rise above 10% in one hour, the system automatically reroutes EU traffic to an alternative acquirer with stronger scheme approval ratios.
Result: Approval rates remain steady without manual intervention.
3. Monitoring Approval Rates: The True Underwriter KPI
Underwriters treat approval rates as a trust index. A merchant maintaining >80% approval consistency for 90 days signals operational control, a key factor in rolling reserve reduction reviews.
To maintain this threshold, merchants must:
- Segment approval reports by acquirer, channel, and BIN.
- Flag recurring soft declines (temporary) vs. hard declines (structural).
- Measure first-pass success rate (approvals without retries).
Payment Mentors’ data from 2024-2025 shows that merchants who actively monitor acquirer approval trends enjoy:
- 18% higher total processed volume
- 23% faster settlement release from acquirers
That’s because consistent approval data builds lender confidence, proof that you’re managing risk at the micro level.
4. Geographic Optimisation: Localising Strategy for Global Consistency
Each acquirer behaves differently depending on region and card scheme. A good acquirer for the UK may underperform in LATAM, while an Asian acquirer may reject EU-issued cards due to scheme restrictions.
To counter this, Payment Mentors employs geo-segmented performance routing, tracking:
- Approval heatmaps by country and time zone.
- Currency mismatch trends (e.g., USD transactions from ZAR cards).
- Regional fraud tolerance thresholds.
Using this intelligence, merchants dynamically adjust routing logic per region, ensuring consistent approval performance across high-risk markets like:
- Africa (M-Pesa, Paystack, Flutterwave)
- EU (SEPA Instant, local IBAN acquirers)
- Asia (NETS, Alipay+)
- LATAM (PIX, MercadoPago)
In short, localisation isn’t just a customer experience tactic. It’s an underwriting survival mechanism.
5. Continuous Optimisation Cycle: The Payment Mentors 5-Step Model
Every merchant connected through Payment Mentors follows a structured optimisation lifecycle:
| Step | Focus Area | Output |
| 1 | Data Collection | Live acquirer, BIN, and latency data feeds |
| 2 | Analysis | Weekly performance and decline pattern review |
| 3 | Route Adjustment | Auto-update routing logic and failover |
| 4 | Validation | Re-test sandbox environment for consistency |
| 5 | Reporting | Share compliance-ready reports with acquirers |
This continuous loop ensures a merchant is always improving, not just compliant, but evolving in sync with acquirer intelligence models.
6. Tools for Real-Time Oversight
For developers, risk officers, and compliance teams, visibility is everything. Payment Mentors’ Performance Command Centre provides a unified dashboard for all risk and performance metrics.
Core Modules:
- Gateway Health Monitor: Real-time uptime and latency tracking.
- Approval Heatmaps: Geographic approval rate visualisation.
- Decline Reason Analytics: Grouped by issuer and BIN country.
- Chargeback Intelligence Feed: Alerts for chargeback clusters.
- Settlement Forecast Panel: Predicts fund release timing per acquirer.
Each module produces regulator-ready exportable reports that satisfy FCA, MGA, and Curacao eGaming audit requirements, reinforcing transparency at every layer.
7. Human Insight Meets Machine Automation
While automation drives consistency, human expertise still defines accuracy. Payment Mentors in-house risk analysts conduct manual portfolio reviews every 30 days, examining anomalies automation can’t interpret, such as behavioural fraud patterns or local regulatory shifts.
These hybrid reviews ensure:
- Faster detection of emerging fraud types (like synthetic ID attacks).
- More informed discussions with acquirer risk teams.
- Data-driven justification for lower rolling reserves.
Automation gives scale.
Human intelligence gives context.
Together, they make underwriters trust you faster.
8. The Business Case for Continuous Performance Management
High-risk merchants often see compliance as a cost, but performance monitoring turns it into profit protection.
In a recent Payment Mentors audit across 40+ high-risk portfolios:
- Merchants using structured performance monitoring saw 11-14% higher approval rates.
- Chargebacks fell by 22% due to proactive routing updates.
- Acquirer relationship renewals improved by 30% due to transparency reporting.
The message is clear: When you manage performance like compliance, acquirers stop treating you as a liability, and start viewing you as a long-term partner.
Continuous monitoring isn’t optional, it’s the heartbeat of high-risk payments.
It aligns technical efficiency with financial trust, ensuring your gateway isn’t just processing, it’s performing.
Acquirers trust merchants who can prove control in real time.
– Payment Mentors Data Strategy Division, 2025
Conclusion
Turning Gateway Intelligence into Long-Term Underwriting Trust
In high-risk payments, approval isn’t the finish line, it’s the beginning of a performance journey. Every transaction, routing rule, and API call contributes to a larger story: how trustworthy your operation appears to acquirers and regulators.
The truth is simple, underwriters fund confidence, not volume. They approve merchants who demonstrate consistent control across all technical and compliance layers.
That’s why gateway optimization isn’t just about technology; it’s about reputation engineering.
A merchant with:
- Clean routing logic,
- Unified KYC/AML data,
- Continuous monitoring, and
- Documented performance transparency
…isn’t just compliant, they’re bankable.
Building Scalable Payment Infrastructure for High-Risk Success
For high-risk merchants, scalability means resilience. Markets evolve, acquirers rotate, and risk appetites change, but a well-architected gateway framework remains adaptive. By leveraging smart routing, cascading logic, and cross-acquirer intelligence, Payment Mentors helps merchants create ecosystems that thrive even under scrutiny.
The result?
- Faster approvals
- Lower rolling reserves
- Higher transaction throughput
- And stronger acquirer confidence
Each system enhancement compounds, turning operational maturity into financial stability.
The Payment Mentors Advantage
Payment Mentors stand at the intersection of compliance and performance, enabling merchants not only to process globally but to process intelligently.
From underwriting consultation to multi-acquirer integration and data-driven optimisation, our solutions are designed for one outcome:
To make high-risk merchants underwriter-ready, every day, every transaction.
Whether you’re expanding your iGaming platform, scaling a forex brokerage, or launching a cross-border subscription model, our gateway intelligence ensures your approvals stay high and your risks stay managed.
The most successful high-risk merchants aren’t the ones that process the most,
They’re the ones that process the smartest.
Payment Mentors’ data-driven, compliance-aligned approach transforms payment gateways from a cost centre into a strategic performance engine, proving that in high-risk.
Trust is earned, one approved transaction at a time.
FAQs
1. What does “multi-channel payment integration” mean for high-risk merchants?
Multi-channel integration means connecting all your payment entry points, e-commerce checkouts, mobile apps, and virtual terminals (MOTO), to a single, unified gateway. For high-risk sectors like iGaming, forex, or adult services, this ensures every transaction follows consistent fraud prevention, KYC, and PCI DSS standards while improving approval rates and operational control.
2. Why is multi-channel processing critical in high-risk industries?
High-risk merchants face higher fraud rates, chargeback exposure, and acquirer scrutiny. A multi-channel setup distributes transactions across acquirers and geographies, improving uptime, resilience, and regulatory compliance. It also delivers smoother customer experiences, such as allowing players to deposit via card, wallet, or phone without friction.
3. What is a multi-acquirer gateway, and how does it help?
A multi-acquirer gateway connects a merchant to several acquiring banks at once. If one acquirer declines or blocks a transaction, the gateway automatically reroutes it to another. This redundancy improves approval ratios, minimises downtime, and protects merchants from single-acquirer dependency, a major risk in high-risk verticals.
4. How does tokenisation improve security and approval rates?
Tokenization replaces sensitive card data with encrypted tokens, preventing exposure of raw PAN details. In high-risk processing, it keeps merchants PCI DSS compliant and enables one-click deposits or recurring billing without re-entering card data. Network tokens also auto-update when cards expire, improving approval rates by up to 10%.
5. What’s the difference between e-commerce, mobile, and virtual terminal channels in risk terms?
- E-commerce: Main exposure is CNP fraud; requires 3DS2 and PSD2 compliance.
- Mobile: Vulnerable to SDK spoofing and malware; demands SDK attestation and biometric authentication.
- Virtual Terminal (MOTO): High manual fraud risk; must use tokenised, role-based access and recorded verification.
Each channel must apply consistent compliance logic to avoid underwriter red flags.
6. How can merchants ensure consistent compliance across all channels?
Use a unified compliance engine that applies the same authentication, encryption, and KYC/AML logic to every channel. This “single compliance brain” stores logs, user identities, and risk scores in one repository, meeting PCI DSS, PSD2, and GDPR requirements simultaneously and satisfying underwriters during audits.
7. Why do underwriters care about unified KYC and AML processes?
Underwriters view fragmented KYC systems as a major risk. If a user verified on mobile can transact unverified via MOTO, the acquirer faces AML exposure. Unified KYC/AML vetting ensures every customer identity is traceable across all channels, which lowers perceived risk and can reduce rolling reserves or reserve periods.
8. What are best practices for integrating mobile payments in high-risk sectors?
- Use PCI DSS 4.0-compliant SDKs with tokenisation.
- Implement mutual TLS and SDK attestation.
- Enable biometric 3DS2 authentication for PSD2 compliance.
- Localise payment options (e.g., M-Pesa, PIX, Paystack).
- Maintain a Mobile Risk Score (MRS) engine for fraud detection.
These ensure regulatory compliance and higher approval rates across global mobile markets.
9. How should merchants manage Virtual Terminal (MOTO) compliance?
Virtual Terminal systems must:
- Operate entirely through web-based PCI-compliant interfaces.
- Use masked card fields and role-based access.
- Log all transactions and agent actions.
- Verify customer identity for large-value payments.
- Record consent to meet FATF and AML obligations.
Proper documentation helps underwriters classify MOTO environments as “controlled” rather than “exposed.”
10. How does real-time performance monitoring improve acquirer trust?
Continuous monitoring of approval rates, decline codes, latency, and chargeback trends allows merchants to detect acquirer or geographic issues early. Platforms like Payment Mentors’ Aegis Performance Layer auto-adjust routing logic to maintain high approval consistency, providing operational control and strengthening underwriter confidence.
11. What are the top KPIs every high-risk merchant should track?
- Approval rate by acquirer
- Decline reason code trends
- Chargeback ratio per channel
- Latency and uptime metrics
- FX spread variance
Tracking these in real time ensures merchants can prove stability and compliance to acquirers during reviews or reserve reduction assessments.
12. How can Payment Mentors support multi-channel integration?
Payment Mentors provides end-to-end multi-channel orchestration, including:
- Multi-acquirer routing and cascading logic
- PCI DSS and PSD2 compliance alignment
- Cross-channel KYC/AML framework
- SmartRoute and Aegis performance monitoring tools
This ensures high-risk merchants process securely, efficiently, and underwriter-ready across all regions.




